FM2DS: Few-Shot Multimodal Multihop Data Synthesis with Knowledge Distillation for Question Answering
▶ ServiceNow Research 1
▶ UBC, Vancouver, Canada 2
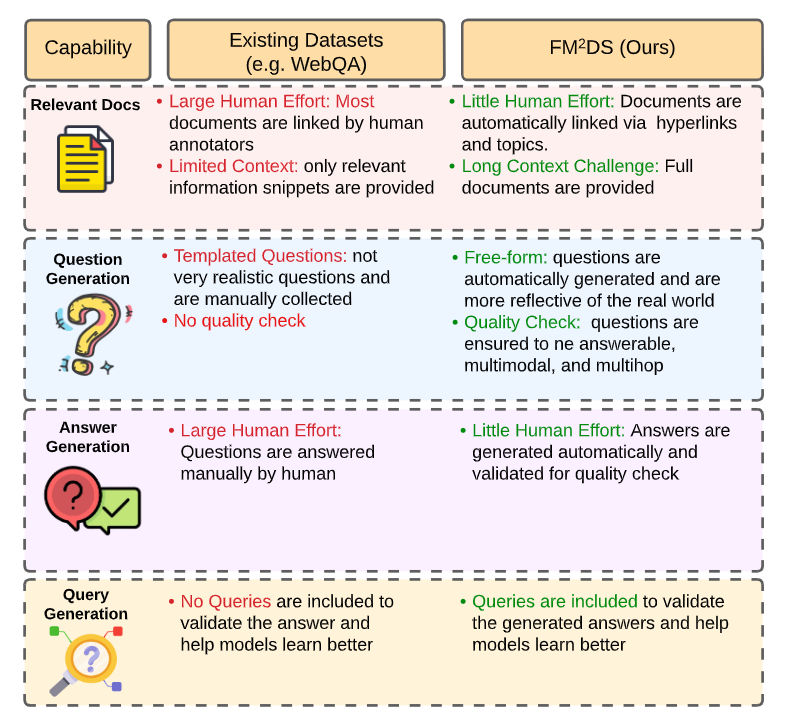
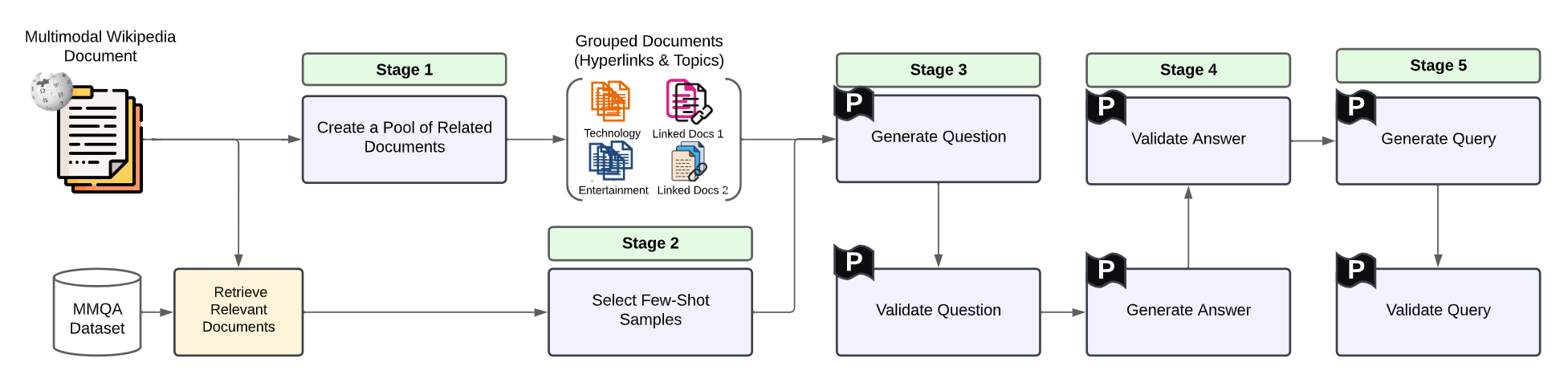
Multimodal multihop question answering is a complex task that requires reasoning over multiple sources of information, such as images and text, to answer questions. While there has been significant progress in visual question answering, the multihop setting remains unexplored due to the lack of high-quality datasets. Current methods focus on single-hop question answering or a single modality, which makes them unsuitable for real-world scenarios such as analyzing multimodal educational materials, summarizing lengthy academic articles, or interpreting scientific studies that combine charts, images, and text. To address this gap, we propose a novel methodology, introducing the first framework for creating a high-quality dataset that enables training models for multimodal multihop question answering. Our approach consists of a 5-stage pipeline that involves acquiring relevant multimodal documents from Wikipedia, synthetically generating high-level questions and answers, and validating them through rigorous criteria to ensure quality data. We evaluate our methodology by training models on our synthesized dataset and testing on two benchmarks, our results demonstrate that, with an equal sample size, models trained on our synthesized data outperform those trained on human-collected data by 1.9 in exact match (EM) on average. We believe our data synthesis method will serve as a strong foundation for training and evaluating multimodal multihop question answering models.

We also propose a benchmark, M2QA, to assess the LVLMs performance on a more complicated MMQA task with full documents. M2QA consists of 500 Q&A pairs, each designed to challenge the model's ability to perform a complex reasoning task. The questions are not templated into a specific structure (as in some existing works like MultimodalQA), instead, they are diverse and challenging. Additionally, answering the questions require access to full documents, where both information extraction and reasoning across different modalities (e.g., images and tables) are essential.
@misc{abaskohi2024fm2dsfewshotmultimodalmultihop,
title={FM2DS: Few-Shot Multimodal Multihop Data Synthesis with Knowledge Distillation for Question Answering},
author={Amirhossein Abaskohi and Spandana Gella and Giuseppe Carenini and Issam H. Laradji},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.07030},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.07030},
}